Background
In today's digital world, internal threats are increasing just like external attacks. These threats are hard to find using traditional security tools, because such tools are mostly built to catch external problems like malware, phishing, or DDoS attacks. Unlike outside attacks that follow known patterns, internal threats often come from trusted users who misuse their access, making it difficult to spot their actions or making them hard to distinguish from normal activities.
As organizations grow and their IT environments become more complex, the volume of user activity and system logs increases exponentially, making manual monitoring impractical. The use of cloud services, remote work, and third-party access makes it even harder to track and manage internal risks. This is where UEBA plays a critical role.
Core Ideas
1. Behavioral Baseline & Anomaly Detection
Detect insider threats by learning normal user behavior patterns and identifying anomalous deviations using machine learning
2. Automated Threat Intelligence Pipeline
Automate data collection, normalization, analysis, and alert generation to flag suspicious internal activities in real-time
System Workflow
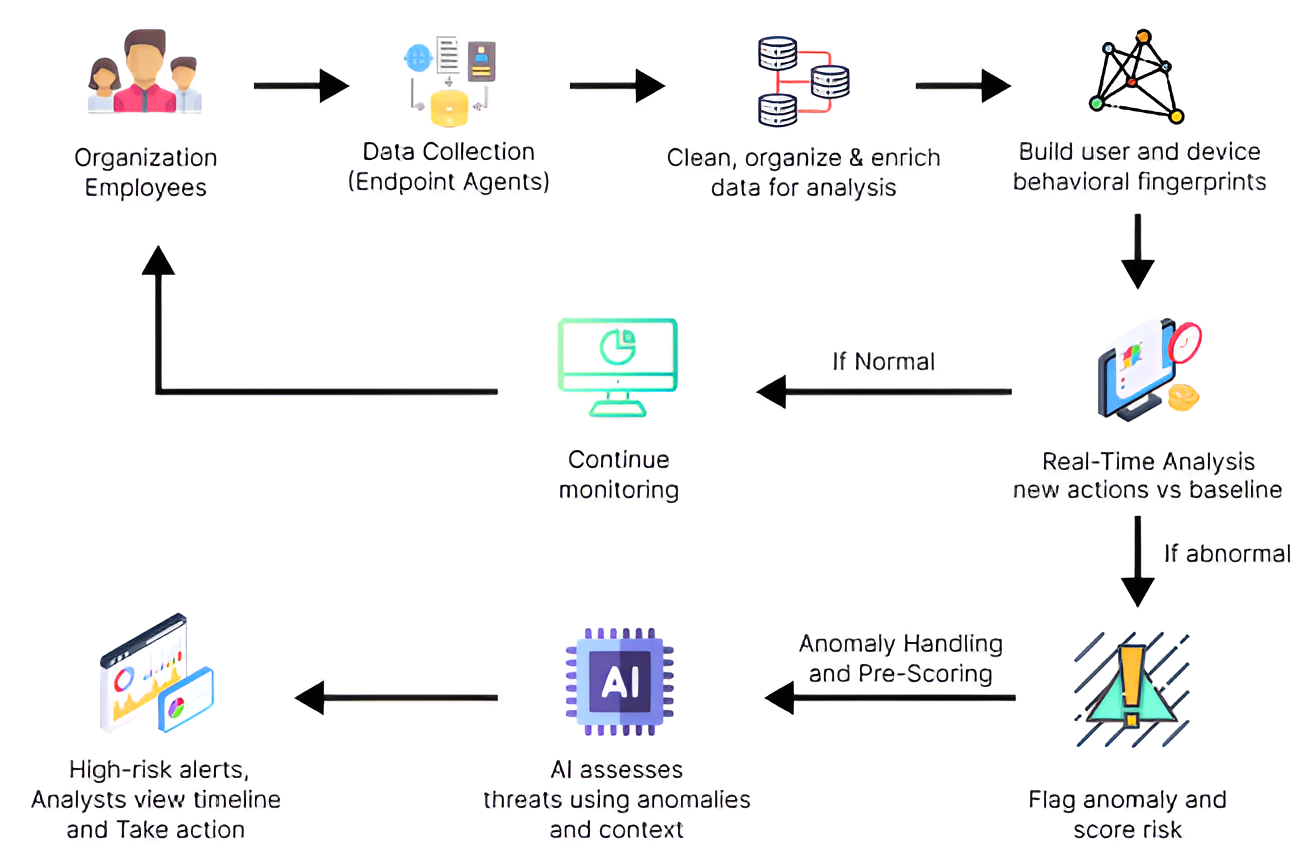
End-to-end workflow showing data flow from user activities to security dashboard
Innovation & Uniqueness
Compare user behavior against peer groups with similar roles to identify subtle deviations
Dynamic risk scoring considering time, location, device type, and organizational changes
Correlate behaviors across multiple entities to detect coordinated insider attacks
Self-updating ML models that adapt to evolving roles and threat patterns automatically
Incorporate typing patterns and mouse movements to detect account takeovers
Proactively simulate insider threat scenarios using historical data
Anonymization and differential privacy techniques for compliance
Human-readable explanations for each anomaly alert for faster response
How it Addresses the Solution
Tech Stack
Technical Architecture
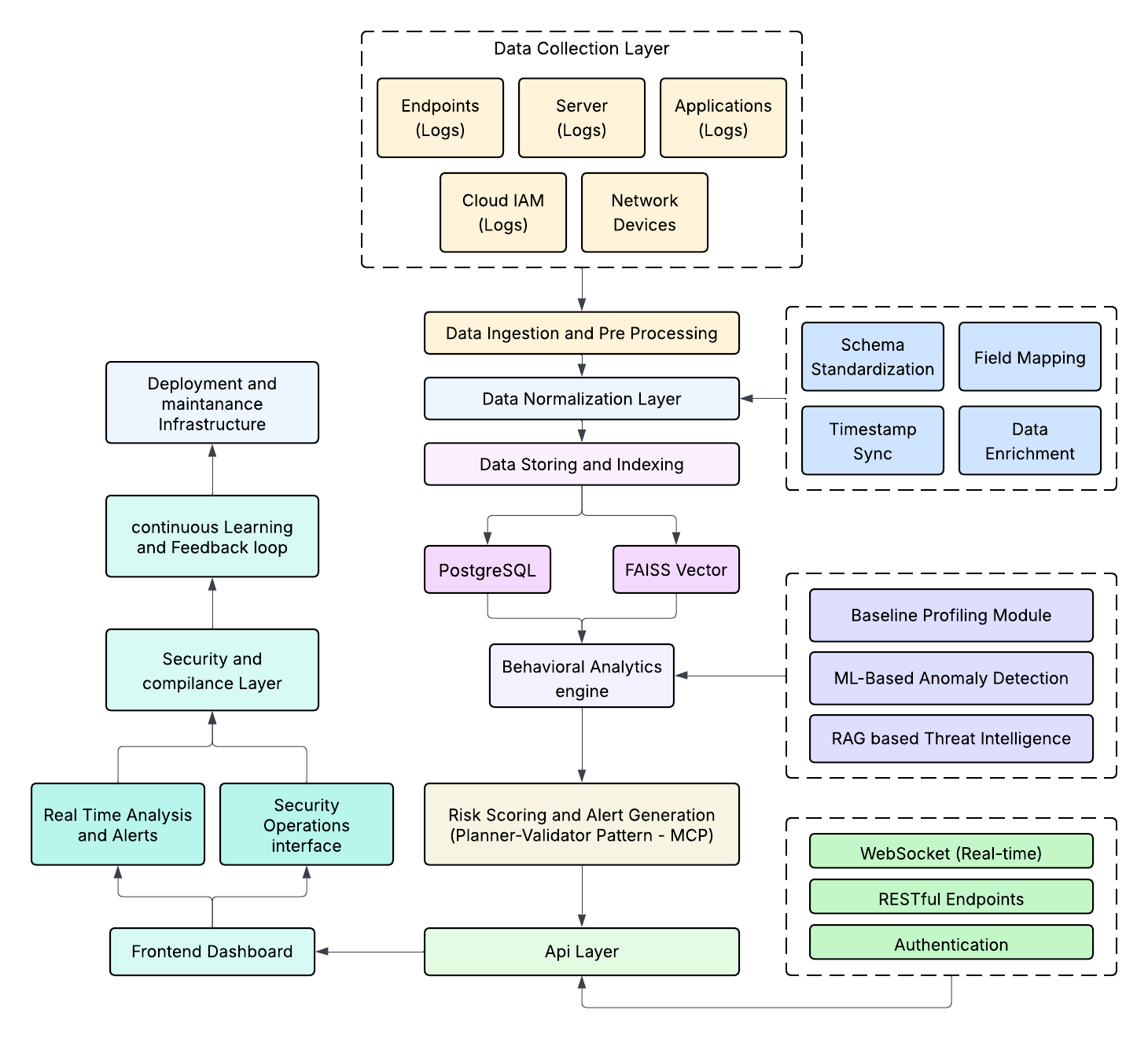
Detailed technical architecture showing all system components and data flow
Use Cases
1. Security Operations Centers (SOCs)
Monitor and respond to behavioral anomaly alerts across the organization in real-time to prevent insider threats.
2. IT Administrators
Track user access patterns and identify suspicious account activities to protect critical systems and infrastructure.
3. Compliance & Regulatory Officers
Audit employee behavior for regulatory compliance and detect policy violations before they escalate into breaches.
4. Government & Defense Agencies
Monitor classified data access and detect unauthorized activities by personnel with security clearances to prevent espionage and data leaks.
5. Incident Response & Forensic Teams
Investigate security incidents using behavioral forensics and historical activity data to understand attack timelines and attribution.
6. Law Enforcement & Intelligence Agencies
Track suspicious insider activities within sensitive operations and identify potential threats to national security infrastructure.
Risk Management
| Risk Category | Potential Challenge | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| AI Reliability | ML models generating false positives or missing actual threats | Continuous model retraining with validated threat data and human-in-the-loop feedback mechanism |
| Data Volume | Massive log data overwhelming processing and storage capacity | Implement data retention policies, log compression, and distributed processing architecture |
| Privacy Compliance | Analyzing employee behavior violating privacy regulations | Anonymization techniques, role-based access controls, and compliance with GDPR/data protection laws |
| Model Drift | Behavioral baselines becoming outdated as user roles evolve | Adaptive learning models with automatic baseline updates and periodic recalibration |
| Alert Fatigue | Too many low-priority alerts overwhelming security teams | Contextual risk scoring, alert prioritization, and tunable sensitivity thresholds |
| Data Security | Unauthorized access to sensitive behavioral data and logs | Full encryption (at rest and in transit), ECDSA for data integrity, and regular security audits |
Existing Approach vs Our Solution
| Aspect | Existing Approach | Our Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Threat Detection | Rule-based SIEM systems flagging known external attack patterns | ML-driven behavioral anomaly detection identifying insider threats and account compromises |
| User Expertise | Requires cybersecurity analysts to manually investigate logs and correlate events | Automated risk scoring with explainable alerts enabling faster response by any security personnel |
| Detection Scope | Focuses on perimeter security and known threat signatures | Analyzes user behavior patterns, peer groups, and contextual factors for hidden threats |
| Alert Quality | High false positive rates causing alert fatigue | Contextual risk scoring and adaptive learning reducing false positives significantly |
| Scalability | Manual monitoring impractical for high-volume, complex IT environments | Automated pipeline processing massive log volumes in real-time across distributed systems |
| Decision Support | Reactive incident response after breaches occur | Proactive threat identification with risk prioritization for prevention and early intervention |
A Feasible and Viable Solution
Feasible Core
The data collection, normalization, and ML-based anomaly detection pipeline are operationally proven, using established technologies like Python, pandas, PostgreSQL, and scikit-learn/TensorFlow to handle high-volume log analysis and behavioral modeling.
Viable Completion
The dashboard and visualization layer for security teams is a low-risk implementation using standard web technologies (Node.js, Express.js, Plotly.js, D3.js), enabling intuitive threat monitoring and alert management with minimal development complexity.
Financial Viability
Lean Costs
Low start-up costs leveraging open-source ML frameworks and cloud infrastructure, with scalable operational expenses optimized through efficient data processing and storage management.
Sustainable Funding
Long-term viability achieved through enterprise licensing models, cybersecurity grants, institutional partnerships, and optional managed service offerings for organizations lacking in-house security expertise.